
|
|
KEYNESIAN CROSS: The standard diagram used in Keynesian economics to identify the equilibrium level of aggregate output (that is, gross domestic product), with aggregate expenditures measured on the vertical axis, and aggregate output measured on the horizontal axis. This diagram contains two key lines, the aggregate expenditure line and the 45-degree line. Intersection between these lines indicates equilibrium aggregate output. This intersection, or cross, is what gives rise to the name.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           PERFECT COMPETITION, SHUTDOWN: A perfectly competitive firm is presumed to shutdown production and produce no output in the short run, if price is less than average variable cost. This is one of three short-run production alternatives facing a firm. The other two are profit maximization (if price exceeds average total cost) and loss minimization (if price is greater than average variable cost but less than average total cost). A perfectly competitive firm guided by the pursuit of profit is inclined to produce no output if the quantity that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost in the short run incurs an economic loss greater than total fixed cost. The key to this loss minimization production decision is a comparison of the loss incurred from producing with the loss incurred from not producing. If price is less than average variable cost, then the firm incurs a smaller loss by not producing that by producing.One of Three Alternatives| Production Alternatives | | Price and Cost | Result |
|---|
| P > ATC | Profit Maximization | | ATC > P > AVC | Loss Minimization | | P < AVC | Shutdown |
Shutting down is one of three short-run production alternatives facing a perfectly competitive firm. All three are displayed in the table to the right. The other two are profit maximization and loss minimization.- With profit maximization, price exceeds average total cost at the quantity that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost. In this case, the firm generates an economic profit.
- With loss minimization, price is greater than average variable cost but is less than average total cost at the quantity that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost. In this case, the firm incurs a smaller loss by producing some output than by not producing any output.
Zucchini ProductionThe marginal approach to analyzing a perfectly competitive firm's short-run production decision can be used to identify the shutdown alternative. The exhibit displayed here illustrates the short-run production decision by Phil the perfectly competitive zucchini grower. | Shutting Down | 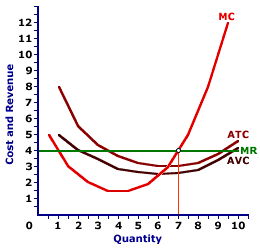 |
The three U-shaped cost curves used in this analysis provide all of the information needed on the cost side of the firm's decision. The demand curve facing the firm (which is also the firm's average revenue and marginal revenue curves) provides all of he information needed on the revenue side.For the time being, Phil faces a $4 price for his zucchinis. As such he produces 7 pounds of zucchinis, which equates the $4 marginal revenue with the marginal cost. However, should this price decline, say to $2.00 per pound, then maximizing a positive profit is not his primary concern. His decision turns to minimizing losses. Click the [$2.00] button to illustrate the situation facing Phil with a lower price. The key to this lower price is that it intersects the marginal cost curve below the average variable cost curve. This is crucial. It means that Phil does not generate enough revenue per pound of zucchinis sold (average revenue = $2.00) to cover the variable cost of producing each pound of zucchinis (average total cost = $2.52). Phil clearly incurs an economic loss on each pound of zucchinis produced and sold. In fact, if Phil produces 5.6 pounds of zucchinis (the quantity that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost), then his total cost is $17.11, but his total revenue is only $11.20. He incurs an economic loss of $5.91, a loss of $1.06 per pound produced. The Short-Run ChoicePerhaps Phil should stop producing. Perhaps he is better off by NOT selling zucchinis. Unfortunately, Phil is faced with short-run fixed cost. Phil incurs a total fixed cost of $3 whether or not he engages in any short-run production. Even if he shuts down production, he still must pay this $3 of fixed cost.As such, Phil is faced with a comparison between the loss incurred from producing with the loss incurred from not producing. Those are his two short-run choices. If he produces, he incurs a loss of $5.91. If he does not produce, he incurs a loss of $3. The choice seems relatively obvious: Phil is better off not producing any zucchinis, incurring an economic loss of $3, and hoping for an increase in the price. Should he produce any zucchinis, he incurs a greater than loss than just paying total fixed cost. Phil does not produce in the short run because he does not generate enough revenue to pay his variable cost, let alone any part of fixed cost. By producing 5.6 pounds of zucchinis, he generates $11.20 of total revenue. This revenue not only falls short of covering the $17.11 of total cost, neither is it enough to pay the $14.11 of total variable cost. This is why the economic loss from production is greater than total fixed cost. Because Phil has no market control, he is subject to the whims of the market price. This $2.00 zucchini price does not generate sufficient total revenue for Phil to pay ALL variable cost, let alone fixed cost. However, should this market price rise, then Phil would have to reevaluate his production decision. If the price rises enough, Phil will be able to produce zucchinis in the short run.

Recommended Citation:PERFECT COMPETITION, SHUTDOWN, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2024. [Accessed: April 27, 2024].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
ORANGE REBELOON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time at a garage sale trying to buy either a microwave over that won't burn your popcorn or a T-shirt commemorating the first day of winter. Be on the lookout for high interest rates.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
The wealthy industrialist, Andrew Carnegie, was once removed from a London tram because he lacked the money needed for the fare.
|

|
|
"Nothing is a waste of time if you use the experience wisely. " -- Auguste Rodin, Sculptor
|

|
PWAC
Present Worth of Annual Costs
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


